
Google Shopping Feed Optimization Guide 2025
- Updated August 2025
- E-commerce Managers, Performance Media Agencies
Google Shopping Feed Optimization (often refered to as Google shopping Feed Management) goes beyond simply creating and managing a compliant feed—it’s about transforming that feed into a competitive advantage. A compliant feed ensures your products can be listed, but an optimized feed ensures they are discovered, clicked, and purchased. By refining titles, enriching attributes, and continuously improving data quality, optimization reduces wasted spend, lowers CPCs, expands reach, and maximizes ROAS.
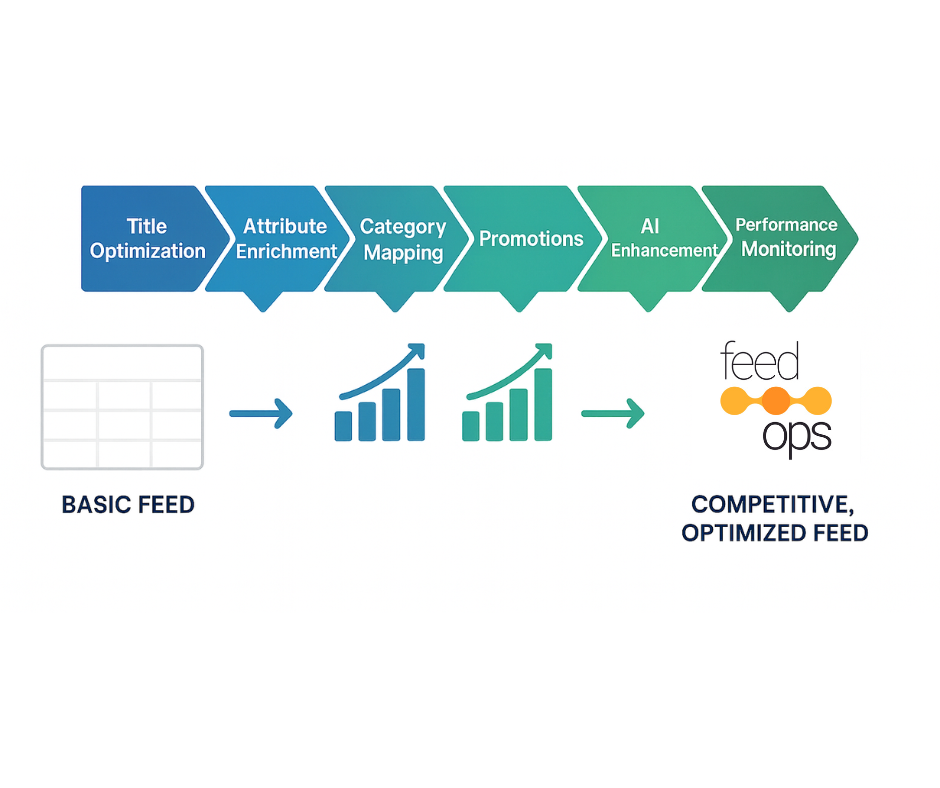
How to turn your feed into a high-perfomance sales engine
Table of contents -
Compliant vs. Competitive Google Shopping Feeds
A compliant feed simply meets Google Merchant Center’s minimum requirements—your products are listed, but without enriched detail, they struggle to surface in competitive auctions. A competitive feed, on the other hand, goes beyond basic eligibility: titles are keyword-rich and intent-driven, attributes are complete, categories are specific, and images meet best practice standards. Competitive feeds not only pass approval but also position products to win impressions, attract clicks, and convert more efficiently.
Google Shopping Feed Optimization reduces CPCs, extends reach, and boosts ROAS.
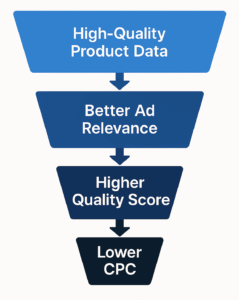
Optimize a product feed for better Ad Relevance and Lower CPC
The Google Merchant Center Help article Provide high-quality data emphasizes the importance of providing accurate and comprehensive product data. It states that doing so “increases its chances of showing for the most relevant search queries.” Similarly, a Google Ads Help article on Quality Score (while primarily for Search ads, the principles apply) highlights that ad relevance—how closely your ad matches a user’s search—is a key component of quality and directly impacts performance. A high quality/relevance score can lead to lower costs per click.
Product Feed Optimization Also Expands Reach and Sales
Google’s own documentation repeatedly confirms that detailed product data expands the reach of your ads. The Merchant Center Help article Tips to optimize your product data explains that when Google understands what you’re selling, it can “serve your Google Shopping ads and free listings in more relevant ways.” It also states that providing important attributes in your product titles helps to “better match search queries and drive performance lift.”
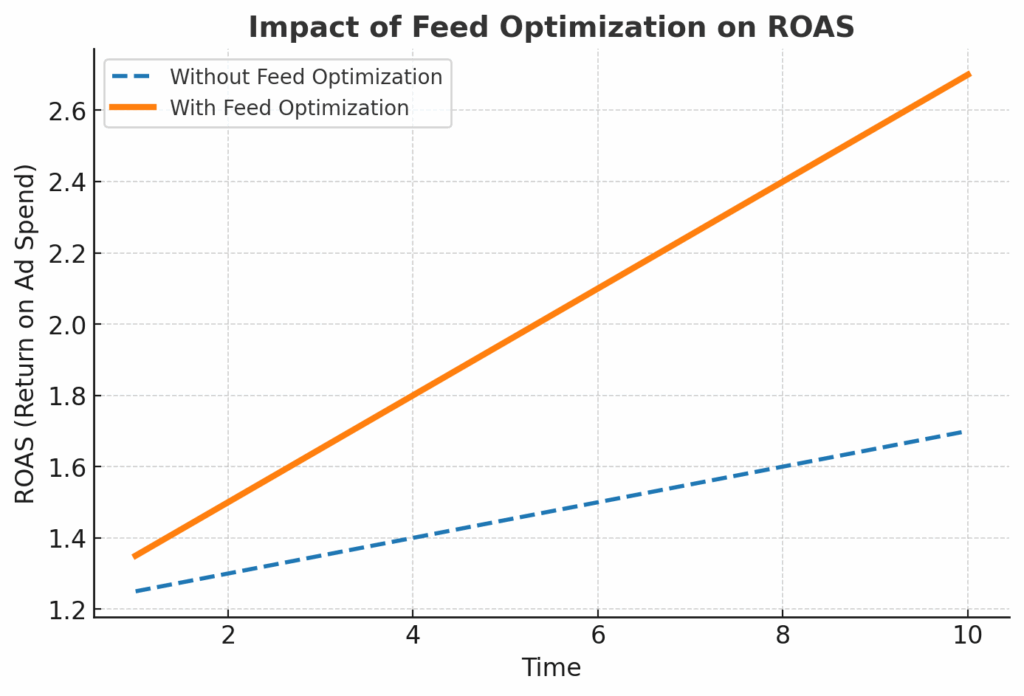
Optimize for Improving ROAS
By improving relevance and expanding reach, you naturally improve your Return on Ad Spend (ROAS). If your quality score is higher, you pay less for each click. If you pay less for your clicks, your conversions will be cheaper. If you can get more conversions for the same cost, your Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS) will increase. This is because you’re driving more qualified traffic that is more likely to convert, reducing wasted ad spend on irrelevant clicks.
Proactive Google Shopping Feed Optimization
Optimizing product feeds is not a one-time task—it’s a process of continuous improvement. Once compliance and eligibility are achieved, the real opportunity lies in proactive optimization. This means constantly refining titles, descriptions, attributes, categories, images, and ensuring new SKUs are fully optimized as they’re added to your catalog.
Optimizing New SKU Additions for Maximum Performance
Crucially, as new SKUs come into stock, they also need to be optimized. The optimization process isn’t limited to existing products; every new product added to your inventory should undergo the same rigorous optimization for its titles, descriptions, attributes, categories, and images. This ensures that new offerings immediately benefit from enhanced visibility and performance in your campaigns.
The Importance of Proactive Google Shopping Feed Optimization
Proactive Google Shopping Feed Optimization focuses on keeping your data fresh, relevant, and enriched to maintain competitive advantage. By treating your feed as a living asset, you ensure that your campaigns not only stay eligible but also continuously improve in efficiency, visibility, and ROAS.
Optimizing Product Titles for Better Google Shopping Campaigns
Strong Google shopping product title optimization is the single most important factor in Google Shopping Feed Optimization. They determine whether your product matches shopper intent and wins impressions in competitive auctions. Titles should balance keyword relevance with readability, ensuring shoppers instantly understand the product while Google’s algorithm identifies it correctly.
Winning Shopping Ads with Title Optimization
Strong product titles are the single most important factor in Google Shopping Feed Optimization. They determine whether your product matches shopper intent and wins impressions in competitive auctions.
A well-optimized title should be a balance of user intent, product definitions, key features, and benefits—all kept under 150 characters (ideally less) to avoid truncation and ensure clarity across all ad formats.
Best practices for Google Shopping product titles:
Balance intent & product clarity: Titles should answer both what the product is and why it matters.
Keyword intent & placement: Use high-intent keywords up front (brand, product type, attributes, variants) while keeping language natural.
Category nuance: In some categories, it makes more sense to start with the product type (e.g., “Running Shoes – Nike Men’s Air Zoom Pegasus 39”) rather than the brand. In others, brand-first performs better.
Layer in key attributes: Add size, color, material, or model when relevant. This improves match rate for long-tail queries and reduces wasted clicks.
Keep it clean: Avoid promotional text, ALL CAPS, or keyword stuffing.
Pro Tip: Think of titles as the “headline” of your Shopping ad: clear, precise, and intent-driven.
Read:Google Shopping Product Title Optimization: 7 Best Practices & Gen AI – For a more in-depth guide
For large catalogs, title templates are essential to maintain consistency and scalability. Templates act as a fail-safe automation layer—they ensure every SKU has a usable, structured title before deeper AI-driven optimization is applied. Platforms like FeedOps make this process automatic, giving retailers a reliable safety net across thousands of products.
When building templates, always consider category nuances first: what works in branded apparel may not work in unbranded homewares. Templates should reflect how customers actually search within that category.
Examples:
Branded Apparel: Brand + Product Type + Key Attributes (Color/Size/Material)
Example: Nike Men’s Running Shorts – Black, Size M
Unbranded Homewares: Product Type + Material/Style + Use Case
Example: Ceramic Coffee Mug – Matte White, 350ml Dishwasher Safe
Pro Tip: Title templates aren’t the end of optimization, but they provide the foundation. Once in place, AI can refine titles further—adding nuance, intent-driven phrasing, and differentiators that give your products the edge in competitive auctions.

AI-Assisted Title Generation in Google Shopping Feed Optimization
AI tools can analyze search trends and shopper behavior to suggest optimized titles at scale. They identify missing keywords, reorder title elements, and localize language for different markets. These systems can work across any language or region, often delivering astonishing results that humans can’t replicate consistently.
Platforms like FeedOps put this power into practice by combining AI with automation. FeedOps can scan entire catalogs, enrich titles with high-intent keywords, and adjust formatting for specific ad surfaces—helping retailers achieve scale, accuracy, and performance uplift across thousands of SKUs.
Pro Tip: Use AI for scale, but always review high-value products manually to ensure titles stay true to brand voice and product accuracy.

Google Product Types in Feed Optimization
Google Product Types are one of the most underutilized levers in Google Shopping Feed Optimization. While Google labels them as “optional,” in practice they are a powerful source of keywords and contextual signals that help Google better understand and match your products to user intent.
Product Type vs. Google Product Category
It’s important to distinguish between the two:
Google Product Category (GPC): A standardized taxonomy set by Google. This is required and ensures eligibility. Google automatically assigns categories using its own AI, based on your product data.
Pro Tip: if Google assigns the wrong category, it’s often a sign your descriptions or titles are too short or lack sufficient detail.Product Type Google Shopping: A merchant-defined hierarchy. Optional on paper, but in reality a valuable signal that can expand reach and improve match quality.
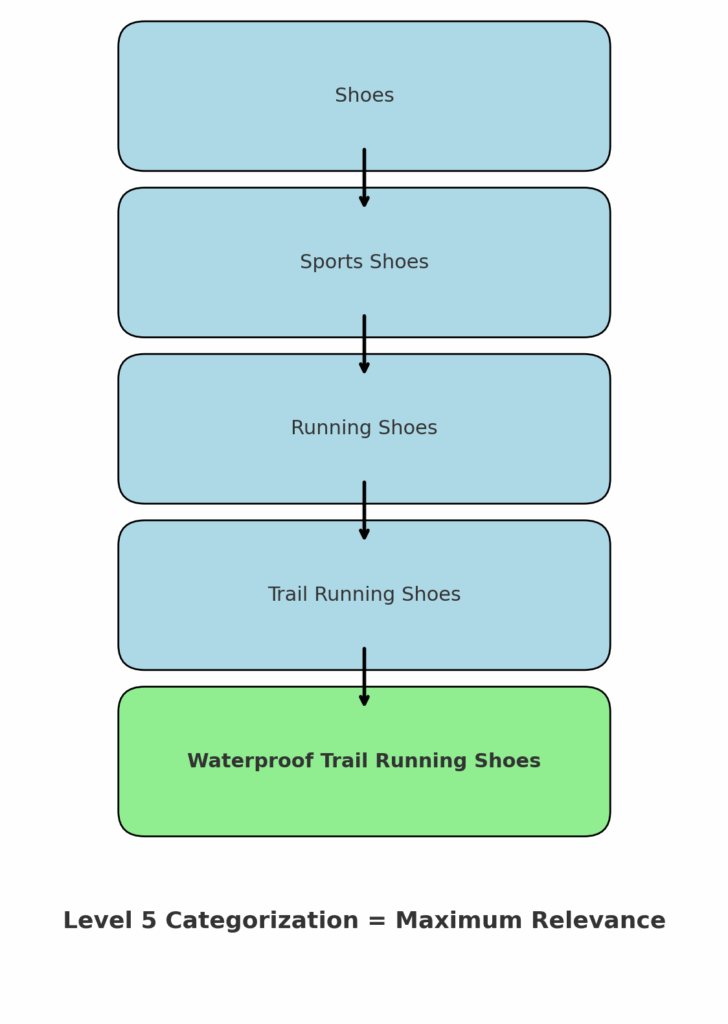
Best Practice: Categorize to the Lowest Level
For best results, always categorize products as deeply as possible (up to 5 levels).
Example: Clothing > Men’s Clothing > Activewear > Shorts > Running Shorts
The deeper the categorization, the stronger the signals Google has to match high-intent queries.
Pro Tip: FeedOps recommends always categorizing to Level 5 where possible. This creates maximum granularity, which increases both reach and relevance in competitive auctions.
AI-Assisted Product Type Categorization
AI often outperforms humans in categorization because it:
Recognizes more categories consistently.
Doesn’t get tired or overwhelmed by cognitive load.
Identifies subtle differences in product data that indicate more precise categorization.
Platforms like FeedOps use AI to automate product type categorization across entire catalogs, ensuring accuracy and scale without the manual grind.
Read: Product Type Google Shopping: How to Optimize for Better ROAS to learn more.
Optimizing Product Data Attributes in Google Shopping
Attributes are a critical layer of Google Shopping Feed Optimization, but they only deliver value when they are relevant to the product being advertised. Just like with titles, attributes should reflect the details that matter most to the shopper’s intent.
For example, pattern is highly relevant for categories like apparel or tablecloths, where shoppers may search for “striped dress” or “floral tablecloth.”
In contrast, pattern has little or no value for workshop equipment, where attributes like dimensions, material, or power source matter far more.
Pro Tip: Apply the same thought process to attributes as you do with titles. Ask: What details help Google classify this product more precisely, and what details help a shopper choose it with confidence?
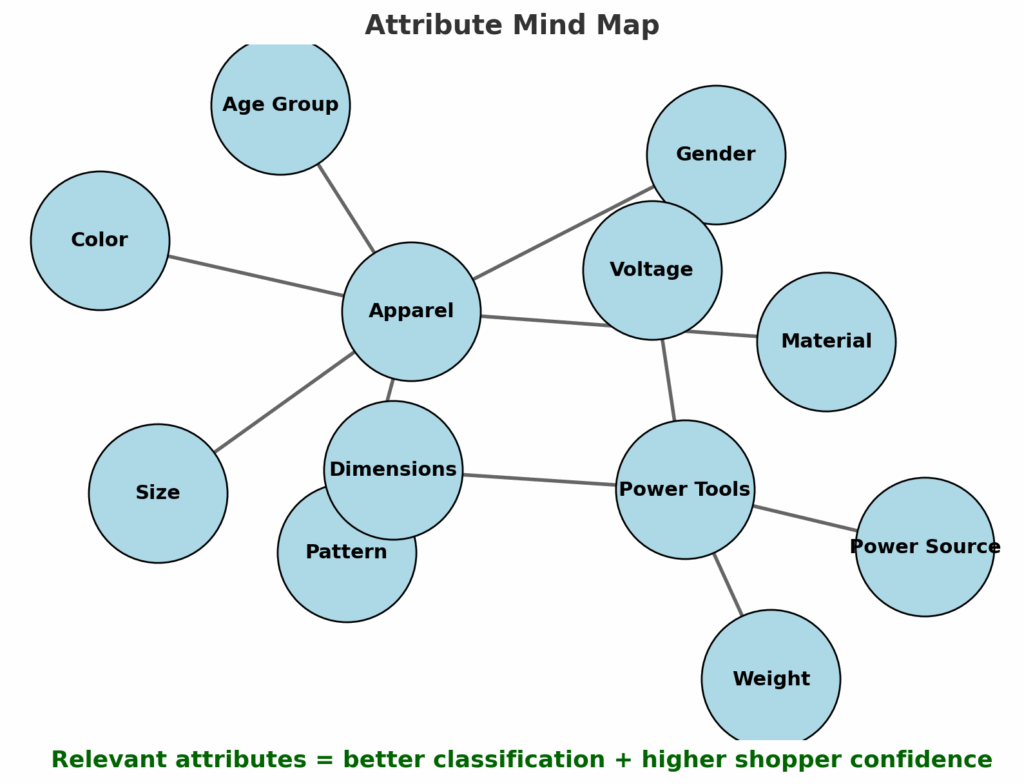
Building an Attribute Matrix for Google Shopping Feed Optimization
The best practice is to build a matrix of relevant attributes for each Google Product Category you sell in. This ensures you capture every attribute that can strengthen your Shopping feed.
Start by listing the required and optional attributes Google suggests.
Identify which ones are actually purchase drivers in your category.
Treat relevant “optional” attributes as mandatory for your process.
Once your attribute matrix is in place, the goal is to ensure those fields are as complete as possible.
Optimizing Product Descriptions in Google Shopping Feed Optimization
An optimized product description is a critical part of your conversion funnel. Once a user clicks on your Shopping ad, they are looking for more information to validate their purchase decision.
Building Confidence
A detailed, well-written description answers a shopper’s implicit questions:
Is this the right size?
What is it made of?
How do I use it?
Does it have the features I need?
By answering these questions proactively, you build trust and confidence.
Highlighting Differentiators
This is where you can showcase what makes your product unique. Is it eco-friendly? Does it come with a lifetime warranty? Is it a limited edition? An optimized description allows you to sell the unique value proposition, not just the product itself.
Improving On-Site Conversion
Although the full description isn’t always visible in the ad, it is displayed on the product page. A well-formatted description on your site leads to a smoother user experience and a higher likelihood of conversion.
Crafting Intent-Rich Descriptions Without Keyword Stuffing
Use Natural, Conversational Language: Think about how a customer would search or ask about a product. Instead of “Men’s T-shirt”, an intent-rich description would say: “This soft, breathable cotton t-shirt is perfect for everyday wear, offering a comfortable fit and a classic crewneck design that never goes out of style.”
Focus on Benefits, Not Just Features: A feature is “12 MP camera.” A benefit is “Capture stunning, high-resolution photos with a 12 MP camera, perfect for printing and sharing on social media.”
Leverage the Long Tail: By using natural language, you organically include long-tail search terms that a user might type.
Pro Tip: Avoid keyword stuffing. Example of what not to do: “Buy cheap red jacket. Best red jacket for sale. Red jacket. Jacket red. Top jacket. Red jacket men’s. Red jacket waterproof. Red jacket winter. Shop red jacket now.” This kind of description is unreadable, provides no value, and may be flagged by Google as low quality.
Leveraging AI to Fill Missing Detail
AI is a game-changer for scalability and consistency in product feed management. Tools like FeedOps can:
Analyze product images, titles, and metadata to generate detailed descriptions.
Fill in missing details (materials, dimensions, features).
Scale across thousands of SKUs while maintaining brand tone and consistency.
Note for Larger Brands: Approval workflows, tone of voice, and guardrails are essential to ensure AI-generated descriptions stay accurate and on-brand.
Formatting for Readability and Relevance
Use short, scannable sentences.
Highlight key features and benefits with bullet points.
Front-load key details (size, color, USP) so they show up even if truncated.
Monitoring Performance in Google Shopping Feed Optimization
You may also like or Google Shopping Ads Management Guide
Optimizing your feed isn’t a “set and forget” task—it’s an ongoing process that requires active monitoring. Even the best-structured feed can drift in performance as new SKUs are added, categories shift, or customer behavior changes.
The first layer of monitoring should always be Google Merchant Center diagnostics—watch for disapprovals, warnings, and missing attributes that can quietly erode visibility. The second layer is Google Ads performance data, where you track impressions, click-through rates, CPCs, and conversion rates to understand how product data impacts campaign efficiency.
FeedOps recommends reviewing this data regularly, not only at the campaign level but at the SKU level, since even small issues can drag down overall results. AI-driven tools can flag anomalies—like sudden drops in impressions for a product or categories where attributes are consistently incomplete—before they snowball into lost revenue.
Final note : Modern ecommerce businesses and ecommerce brands rely on accurate product information and a well-structured product data feed to reach potential customers across Google surfaces. Whether you’re using Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento, or a custom integration, optimizing your feed attributes and fixing feed errors directly improves product visibility in both paid and organic listings on the Shopping tab. Every detail matters—from product identifiers and descriptions to accurate categories that match specific search queries. Skilled Google Shopping specialists understand that consistent data mapping and proactive monitoring enhance customer engagement and ensure your products appear in relevant search results. Even subtle improvements, like refining attribute formatting or checking the “skip navigation” structure of your landing pages, can help businesses stand out among competitors. In short, strong feed management isn’t just about compliance—it’s about building an ecosystem where every product field, attribute, and keyword works together to convert impressions into measurable sales.
Related Demos
Google Shopping Feed Optimization FAQs
What is the difference between feed management and Google Shopping feed optimization?
Feed management ensures your products are connected and approved in Google Merchant Center. Google Shopping feed optimization goes further by enhancing product titles, attributes, descriptions, and categories to improve relevance, lower CPCs, and increase sales performance.
Do I need Google Shopping feed optimization if my products are already approved?
Yes. Approval only makes products eligible to show, but it doesn’t guarantee visibility or clicks. Google Shopping feed optimization improves how your products match search intent, helping them appear for the right queries and convert more efficiently.
How often should I optimize my Google Shopping feed?
Feed optimization is not a one-time task. You should optimize continuously, especially when adding new SKUs, updating stock levels, or launching promotions. Regular optimization keeps your data accurate and competitive, ensuring maximum ROAS.
How does AI help with Google Shopping feed optimization?
AI tools can enrich product data by filling missing attributes, generating optimized product titles, and categorizing products at scale. This improves feed accuracy and saves time. However, manual review of high-value or branded products is still important to protect accuracy and brand tone.
What is the difference between Google Product Types and Google Product Categories?
Google Product Categories are required and come from Google’s taxonomy.
Google Product Types are optional but highly valuable. They are merchant-defined and provide extra keywords and context that improve ad targeting and reach.
Can promotions or sales improve my Google Shopping ad performance?
Yes. Promotions, discounts, and competitive pricing can positively impact both your paid Shopping ads and free product listings. Google rewards complete and compelling product data, including promotional details.
What is the difference between Local Inventory Ads and Local Area Feeds?
Local Inventory Ads (LIA): Show real-time store-level availability and pricing for nearby shoppers.
Local Area Feeds: Allow different prices in different regions for online sales, even without physical store data.
Is Google Shopping feed optimization necessary for small catalogs?
If you have fewer than 100 SKUs, a basic feed plugin may be enough. But if you manage thousands of SKUs or invest heavily in ads, using a platform like FeedOps ensures advanced optimization that improves efficiency, lowers CPCs, and increases sales.
Does feed optimization improve organic Google Shopping results as well?
Yes. The same product data powers both paid ads and free Google Shopping listings. Optimizing your feed improves visibility in both, driving additional free traffic alongside your paid campaigns.
Can Google Shopping feed optimization reduce wasted spend in Performance Max (PMax) campaigns?
Absolutely. By aligning product data with shopper intent, Google Shopping feed optimization helps PMax campaigns prioritize high-intent searches, reduce irrelevant clicks, and deliver stronger ROAS.

